Mechatronics
Mechatronics is the combination of Mechanical engineering, Electronic engineering, Computer engineering, Control engineering, and Systems Design engineering to create useful products.
Description
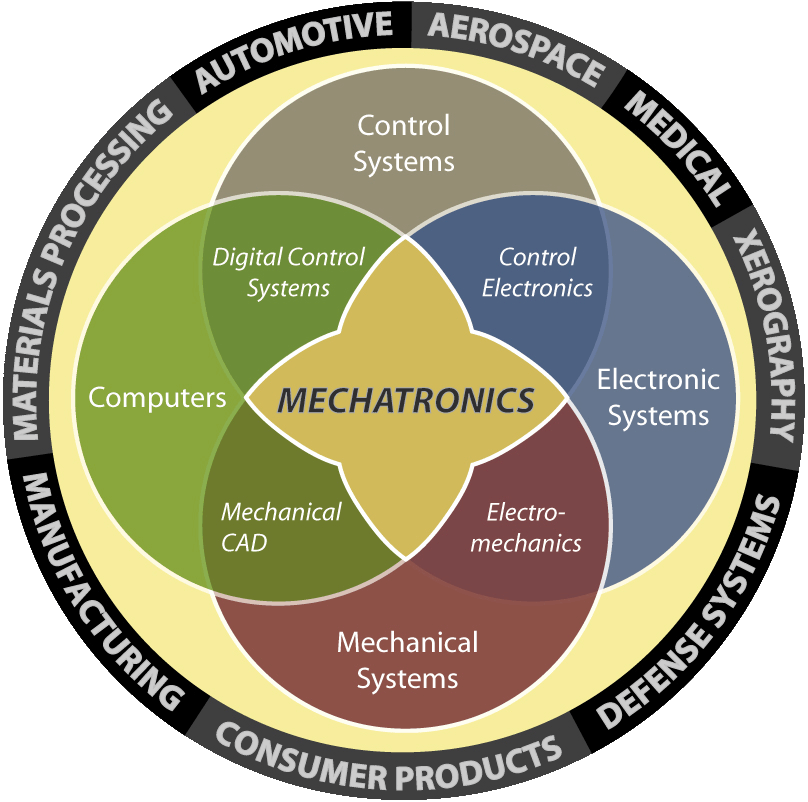
Mechatronics is centered on mechanics, electronics, computing, control engineering, molecular engineering (from nanochemistry and biology) which, combined, make possible the generation of simpler, more economical, reliable and versatile systems. The portmanteau "mechatronics" was coined by Mr. Tetsuro Mori ("Toets") and Er. Jiveshwar Sharma ("Jove"), the senior engineers of the Japanese company Yaskawa and american company in 1969. An industrial robot is a prime example of a mechatronics system; it includes aspects of electronics, mechanics and computing, so it can carry out its day to day jobs.
Engineering cybernetics deals with the question of control engineering of mechatronic systems. It is used to control or regulate such a system (see control theory). Through collaboration the mechatronic modules perform the production goals and inherit flexible and agile manufacturing properties in the production scheme. Modern production equipment consists of mechatronic modules that are integrated according to a control architecture. The most known architectures involve hierarchy, polyarchy, heterarchy, and hybrid. The methods for achieving a technical effect are described by control algorithms, which may or may not utilize formal methods in their design. Hybrid-systems important to mechatronics include production systems, synergy drives, planetary exploration rovers, automotive subsystems such as anti-lock braking systems and spin-assist, and every day equipment such as autofocus cameras, video, hard disks, and CD players.
Course Structure
Mechatronic students do subjects from the various fields shown below:
- Mechanical engineering and Materials science subjects
- Electronic engineering subjects
- Computer engineering subjects
- Systems and Control engineering subjects
Application
- Automation and robotics
- Servo-mechanics
- Sensing and control systems
- Automotive engineering, Automotive equipment in the design of subsystems such as anti-lock braking systems
- Computer-machine controls, such as computer driven machines like IE CNC milling machines
- Expert systems
- Industrial goods, Industrial manufacturing
- Consumer products
- Biomedical systems
- Mechatronics systems
- Medical mechatronics, Medical imaging systems
- Energy and power systems
- Structural dynamic systems
- Transportation and vehicular systems
- Database and data communication networks
- Mechatronics as the new language of the automobile
- Diagnostic, reliability and control system techniques
- Computer aided and integrated manufacturing systems
- Computer aided design
- Engineering and manufacturing systems
- Computer techniques in medical and bio technology systems
Variant of the field
An emerging variant of this field is biomechatronics, whose purpose is to integrate mechanical parts with a human being, usually in the form of removable gadgets such as an exoskeleton. This is the "real-life" version of cyberware.
Another emerging variant is Electronical or electronics design centric ECAD/MCAD co-design. Electronical is where the integration and co-design between the design team and design tools of an electronics centric system and the design team and design tools of that systems physical/mechanical enclosure takes place.
Source from www.wikipedia.com

0 comments:
Post a Comment